Let's Talk Scientific Solutions
Data and summary
- Grid System of National Power Grid of Bangladesh
The power generated at different power stations is transmitted through a national grid system (230 kV & 132 kV) operated and maintained by Power Grid
Company of Bangladesh Limited (PGCB). At present, the national grid system has the capability to handle a maximum load of about 10,000 MW.
The grid system of Bangladesh has a National Load Dispatching Center (NLDC) located in Aftabnagar, Rampura, Dhaka. According to the plan, 400 kV
transmission lines are going to be hooked up with the grid system in the near future. The 400 kV lines will mainly be used to import electric power from India.
Some of the key parameters of the above grid system are given below:
As per the present power system expansion plan, the dependable generation capacity of the country will be about 12 000 MW against a maximum demand of
about 11 000 MW in 2017. The installed capacity is projected to increase to about 33 000 MW by 2030. It is expected that by 2020, the contribution from nuclear
generation will be about 2000 MW and by 2030, it will be increased to about 5 000 MW. Keeping all the above in mind the PGCB needs to take up measures to
upgrade the national grid so as to make it compatible with the generation capacity of the country and in particular, make the grid ready for accommodating the
upcoming NPP by 2023 and a second unit by 2024. For this purpose, detailed power system studies including load flow studies, transient stability studies, long
duration system dynamics studies involving loss of generation, etc., have already been conducted and PGCB is going to make necessary modifications and
renovations in the grid system to make it compatible for the Rooppur NPP.
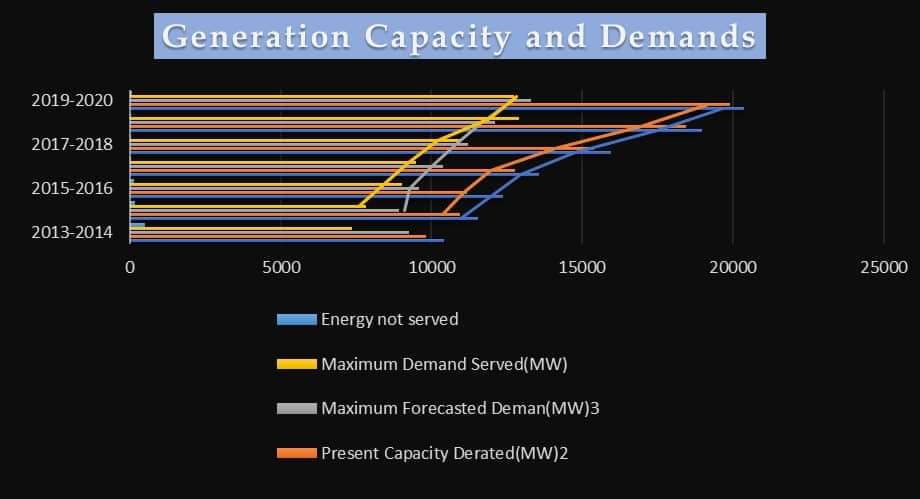
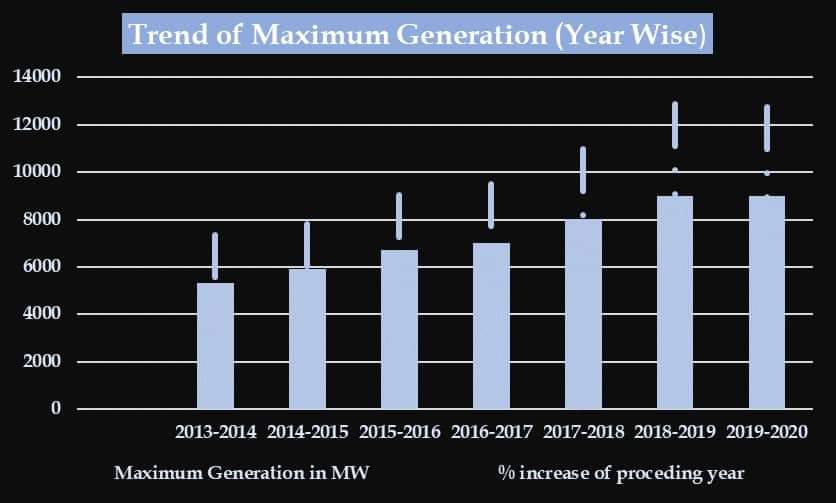
Generation Data of National Power Grid
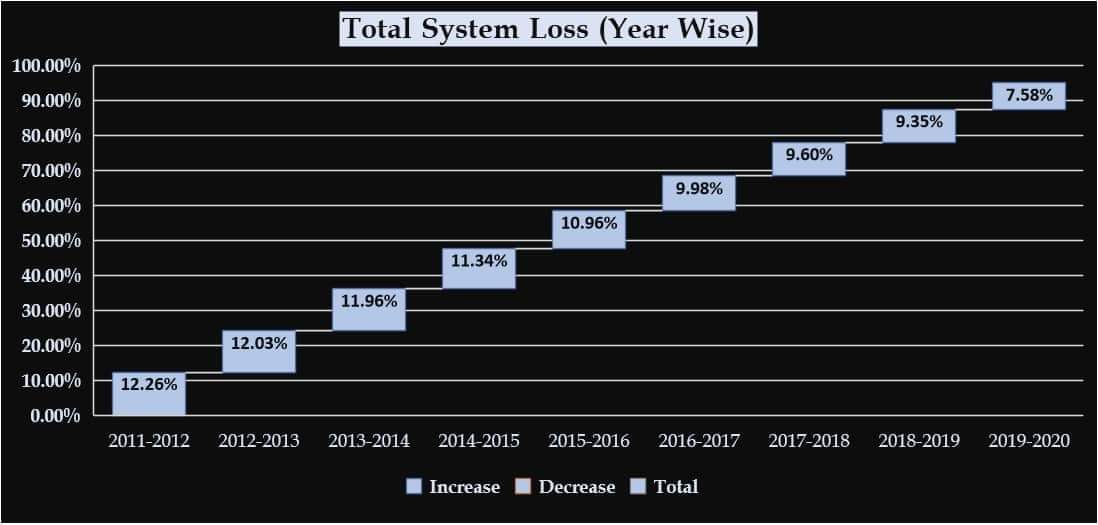
Generation Supply and System Loss
- Grid System of National Power Grid of Bangladesh
How to make flexible electricity through our solution
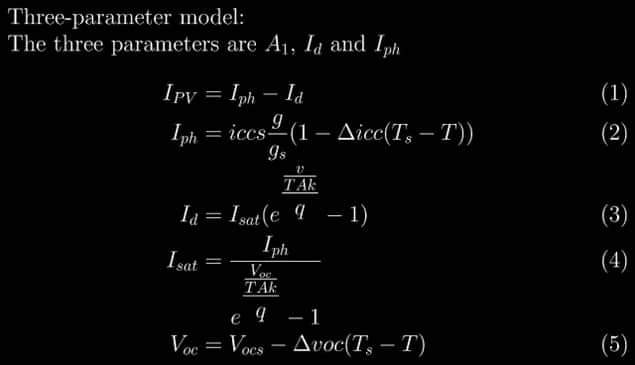
- Three Parameter Model:
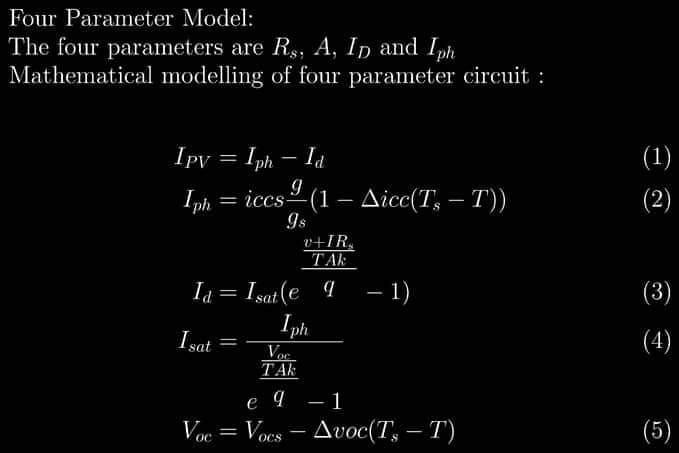
- Four Parameter Model:
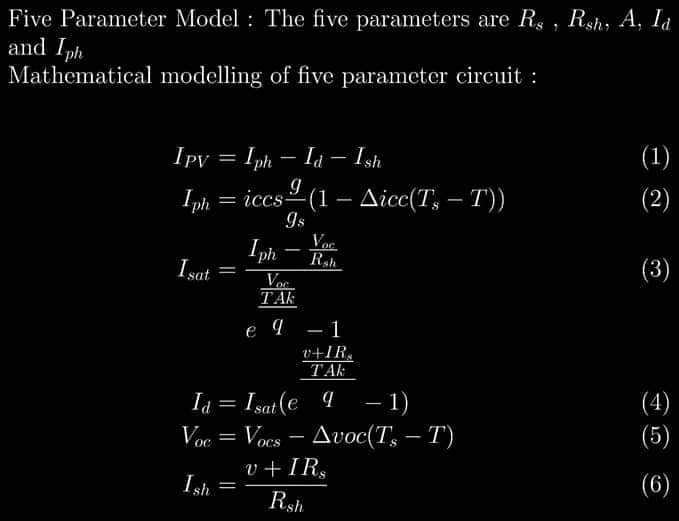
- Five Parameter Model:
- Through coal-solar hybrids
- Through coal-natural gas co-firing
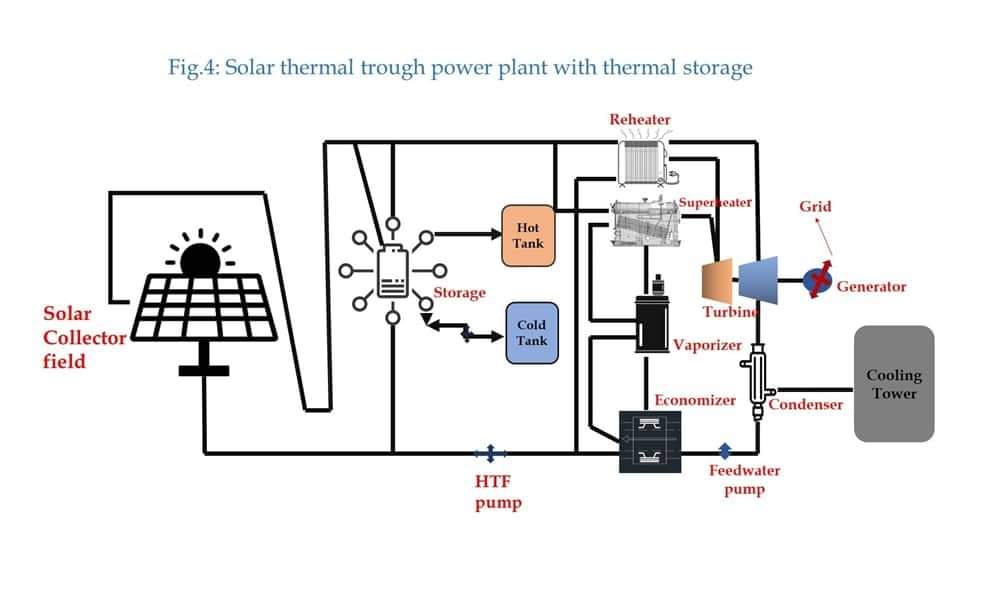
Solar energy is usually harvested in one of two ways. The first is via conventional PV cells that convert solar radiation directly into electricity. The second is solar thermal, usually in the form of concentrated solar power (CSP), where radiation is used to produce heat (Fig. 4). These systems generally rely on a series of lenses or mirrors that automatically track the movement of the sun. They focus a large area of sunlight into a small concentrated beam that can be used as a heat source for a conventional thermal power plant. Implementing equational result of solar energy loss utilization from sunlight is given below in the lesson learned section.
Coal-natural gas co-firing technique can be instrumental in improving operational flexibility and reducing emissions. The EPA has advised that new emissions standards could be met by cofiring ~40% natural gas in highly efficient supercritical pulverized coal power plants. However, some industry observers think that more than this level would be needed and that, for this to be achievable, the boiler would need to be specifically designed to operate in this manner.
Various technical issues will need to be considered when a switch to cofiring is contemplated. For example, there can be significant impacts on heat transfer within the boiler.
II. Possible methods of scaling down coal